2.1.1. Manufacturer-Supplier Dynamical Network Simulation.¶
This function simulates a Manufacturer-Supplier (MS) dynamical network.
-
dynamical_networks.simulate.MS_network.MS_network(A_MS, M_arr, S_arr, make_gif=False, make_graph_plot=False)[source]¶ This function takes system parameters to develop a time dependent adjacency matrix A(t).
- Parameters
A_MS (array) – Unweighted adjacency matrix for network.
M_arr (array) – Throughput array for manufacturers.
S_arr (array) – Throughput array for suppliers.
- Kwargs:
plotting (bool): Plotting for user interpretation. defaut is False.
- Returns
A, an n by n matrix A over time t.
- Return type
(matrix)
-
dynamical_networks.simulate.MS_network.MS_simulation(t, parameters)[source]¶ This function takes system parameters to develop a time dependent throughput simulation of manufacturers and suppliers.
- Parameters
parameter (float) – system parameter or parameters.
t (array) – time array for simulation.
- Kwargs:
plotting (bool): Plotting for user interpretation. defaut is False.
- Returns
Arrays of t for the throughput of manufacturers and suppliers.
- Return type
(M and S arrays)
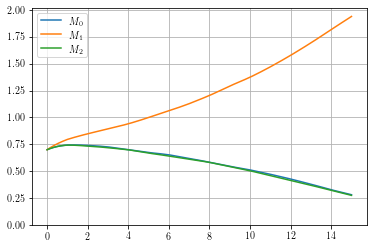
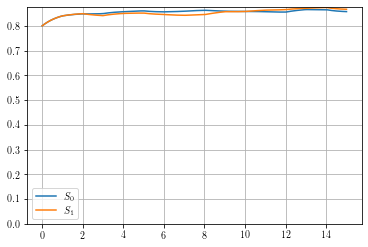
The following is an example simulation of the supplier-manufacturer dynamical network:
from dynamical_networks.simulate.MS_network import MS_simulation, MS_network
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#----------------------System Parameters and intial conditions------------------------
M = np.zeros((3,))+0.7 #current throughput of manufacturer
S = np.zeros((2,))+0.8 #current throughput of supplier
m = len(M)
s = len(S)
a = np.ones(s*m)
a[:int((m*s)*0.65)] = 0
np.random.shuffle(a)
A_MS = a.reshape((m,s)) #adjacency matrix for M/S connections
for i in range(len(A_MS)):
if np.sum(A_MS[i]) == 0:
j = int(np.random.uniform(0,len(A_MS[i]),1))
A_MS[i][j] = 1
for i in range(len(A_MS.T)):
if np.sum(A_MS.T[i]) == 0:
j = int(np.random.uniform(0,len(A_MS.T[i]),1))
A_MS[j][i] = 1
K_M = np.zeros((m,))+2 #maximum throughput of manufacturer
K_S = np.zeros((s,))+1 #maximum throughput of supplier
alpha_M = 0.01 #internal perturbation of manufacturer
alpha_S = 0.01 #internal perturbation of supplier
B_M1 = np.zeros((m,m))+0.6 #effects of price competition on manufacturer
B_S1 = np.zeros((s,s))+0.6 #effects of price competition on supplier
B_M2 = np.zeros((m,m))+0.0 #effects of technology competition on manufacturer
B_S2 = np.zeros((s,s))+0.0 #effects of technology competition on supplier
mu_M = np.zeros((m,)) #Manufacturer production outsourcing intensity
mu_S = np.zeros((s,)) #Supplier production outsourcing intensity
h = 2
# package parameters and define time array
parameters = [M, K_M, alpha_M, B_M1, B_M2, mu_M,S, K_S, alpha_S, B_S1, B_S2, mu_S, h, A_MS]
fs, L = 300, 15
t = np.linspace(0, L,int(L*fs))
#run simulation
M_arr, S_arr = MS_simulation(t, parameters)
A = MS_network(A_MS, M_arr, S_arr)
#plot resulting simulation throughput
for i in range(len(M_arr[0])):
plt.plot(t, M_arr.T[i], label = r'$M_{'+str(i)+'}$')
plt.legend()
plt.ylim(0,)
plt.grid()
plt.show()
for i in range(len(S_arr[0])):
plt.plot(t, S_arr.T[i], label = r'$S_{'+str(i)+'}$')
plt.legend()
plt.ylim(0,)
plt.grid()
plt.show()
Where the output for this example is:
Figure results for M_arr and S_arr